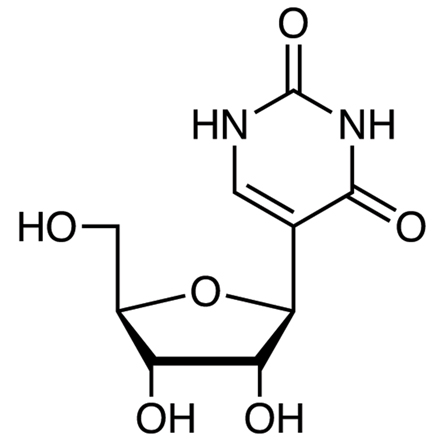
Pseudouridine (5-ribosyluracil, abbreviated by the Greek letter psi- Ψ), the most common modified nucleoside in RNA, is the C-glycoside isomer of the ribonucleoside uridine [
U0020]. Pseudouridine is biosynthesized from uridine via the action of pseudouridine synthases
in vivo. Nowadays, pseudouridine is identified as a fifth nucleoside in RNA. Pseudouridine is found in lots of tRNAs and rRNAs but never in mRNA. However, recently it has been reported that artificial pseudouridylation dramatically affects mRNA function. The function of pseudouridine is currently not clear, but it is assumed that pseudouridine plays a role in association with RNA stability and/or helping aminoacyl transferases interact with tRNAs.