Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.198
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
A halogen group bonded to an aromatic ring is one of the most basic functional groups, and is important as the starting point for Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling and other related reactions.1) For this reason, halogenating reagents are one of the most important reagents, and more efficient halogenating reagents are required. In recent drug discovery research, it has been reported that the introduction of a chloro group into a compound significantly improves its lipophilicity and inhibitory activity, and this has been named the "magic chloro effect".2) This effect, along with the "mimic effect" and "block effect" of the fluoro group and the "magic methyl effect" of the methyl group, is an important approach in discovery research. In addition, halogen groups are also useful in the development of functional materials, improving electronic properties through their electron-withdrawing effect and imparting flame retardancy.3)
Conventional chlorinating reagents include molecular chlorine (Cl2), NCS, DCDMH, SO2Cl2 and tBuOCl. Brominating reagents include molecular bromine (Br2), NBS, DBDMH, etc. A lot of improved reaction conditions have been reported, such as activation with Lewis acids or Lewis bases and the addition of metal catalysts.4) However, with the recent decrease in target proteins and the diversification and complexity of compounds, there are an increasing number of cases where more difficult halogenation is required.
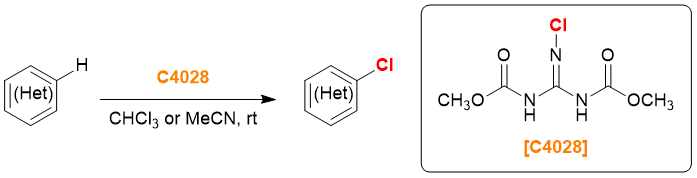
2-Chloro-1,3-bis(methoxycarbonyl)guanidine (Product No. C4028 is a chlorinating reagent called Palau'amine, as it was developed during the total synthesis of the alkaloid, Palau'Chlor.5,6) C4028) is highly active because the chlorine atom is highly activated by the electron-deficient guanidine skeleton, and the leaving group has a high leaving ability.
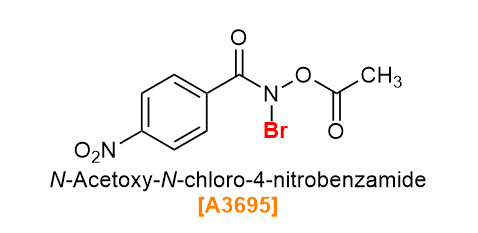
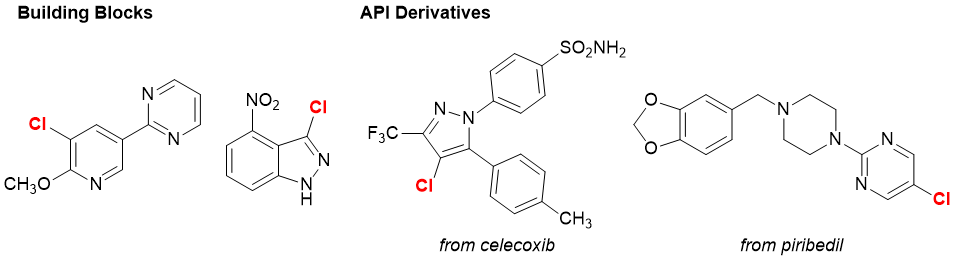
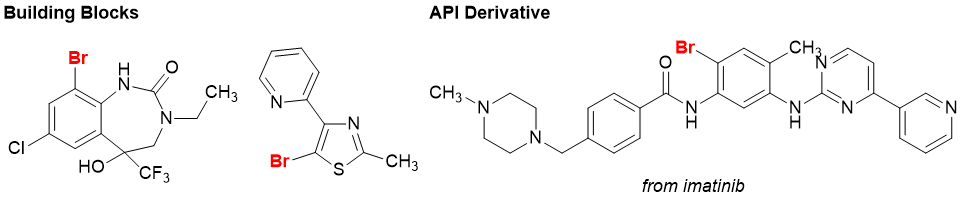
N-Acetoxy-N-chloro-4-nitrobenzamide (Product No. A3694) and N-Acetoxy-N-bromo-4-nitrobenzamide (Product No. A3695) are chlorinating and brominating agents respectively that were recently developed,7) and are characterized by their anomeric amide skeleton. Anomeric amides have a distorted pyramidal structure, and are extremely reactive due to the driving force of planarization and sp2 characterization after elimination. A3694 and A3695 make it possible to halogenate heteroaromatic ring compounds that can not be halogenated with conventional halogenation reagents and conditions. The regioselectivity is high, and in many cases the most electron-rich carbon reacts. It has also been reported that the reaction site can be predicted by the chemical shift of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).8) In addition, the chlorination of celecoxib by flow synthesis using A3694 has been reported,7) so it can be applied to continuous production.
Products
Advantages
- Easy-to-handle solid
- Enables the regioselective halogenation of drug-like complicated hetero aromatics in mild conditions
- Applicable to multi-gram scale synthesis and continuous flow technique
- Suitable for late-stage functionalization in drug discovery research
Applications
Chlorination with C4028 6)

Chlorination with A3694 7)

Bromination with A3695 7)

Related Product Category Pages
Product Brochure
References
- 1) Cross-Coupling and Related Reactions: Connecting Past Success to the Development of New Reactions for the Future
- 2) "Magic Chloro": Profound Effects of the Chlorine Atom in Drug Discovery
- 3) Degradation of the Polymeric Brominated Flame Retardant "Polymeric FR" by Heat and UV Exposure
- 4) Selective Halogenation Using an Aniline Catalyst
- 5) Scalable, stereocontrolled total syntheses of (±)-axinellamines A and B
- 6) Palau'chlor: a practical and reactive chlorinating reagent
- 7) Discovery of N-X anomeric amides as electrophilic halogenation reagents
- 8) Computational Methods to Predict the Regioselectivity of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions of Heteroaromatic Systems