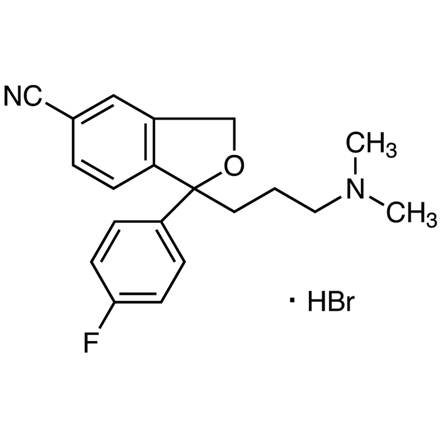
Citalopram hydrobromide is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). It is a racemic bicyclic phthalane derivative consisting of a 1:1 mixture of the
R(-)- and
S(+)[
E0958] -enantiomers. The mechanism of action of citalopram HBr as an antidepressant is presumed to be linked to potentiation of serotonergic activity in the central nervous system (CNS) resulting from its inhibition of CNS neuronal reuptake of serotonin (5-HT) [
S0370].
In vitro and
in vivo studies suggest that citalopram a highly SSRI with minimal effects on norepinephrine (NA) [
A0906] and dopamine (DA) [
A0305] neural reuptake. In additon, citalopram has no antagonistic activity towards DA, NA, 5-HT, histamine [
H0146,
H0147], GABA [
A0282], acetylcholine [
A0084, chloride], and morphine receptors. Although, the inhibition primarily due to the active
S(+)-enantiomer, it is reported that the
R(-)-enantiomer counteracts the activity of the
S(+)[
E0958] -enantiomer. (The product is for research purpose only.)