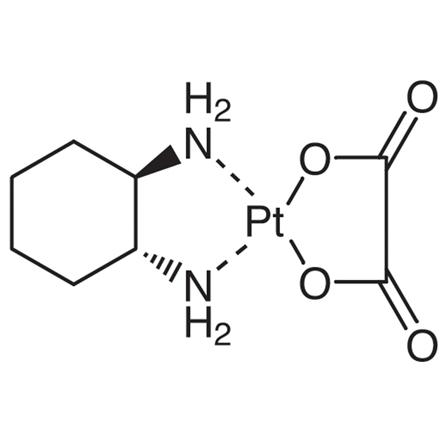
The development of platinum coordination complexes as antitumor agents began in the 1960s, and the highest antitumor activity was exhibited by cisplatin [
D3371], approved by FDA in 1978. Improved versions carboplatin [
C2043] and oxaliplatin were developed to avoid the serious side effects and the problem with resistance associated with the use of cisplatin.
1-5) The platinum complexes diffuse to the tumor cell, where they undergo hydrolysis displacement of their one chloride or carboxylate group leading to a platinum cation. The resulting cation coordinates to the guanine
N7-position of DNA give a coordination cation. Then, intrastrand cross-linking occurs to anther guanine via further hydrolysis displacement of the remaining chloride or carboxylate. The forming [Pt(NH
2R)
2]
2+ ― DNA complex distort the DNA helix (Fig. 1 and 2)
6). Thus, DNA duplication is hindered, which ultimately triggers tumor cell apoptosis.
3)