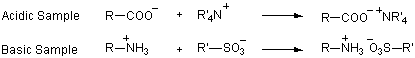Ion-exchange chromatography systems have previously been utilized in HPLC analysis of ionic samples. Reversed phase partition chromatography using ion-pair reagents has been developed and utilized. The ionic samples form an ion-pair with ion-pair reagents in the mobile phase to become electrically neutral. The increase in hydrophobic character of the ion-pair results in a greater affinity for the reverse stationary phase and leads to sample resolution.
UV and fluorescence detectors are widely used. Therefore ion-pair reagents must lack UV absorption and fluorescence themselves to obtain highly sensitive detection of samples. The UV absorption of sodium alkanesulfonates and quaternary ammonium salts is minimal so that these reagents can be used for reliable HPLC analysis. On the other hand, when a sample lacks sufficient UV absorption or fluorescence, the use of
IPA-DAS (Product No. A5701) allows for high-sensitivity detection as a fluorimetric ion-pair reagent.
The use of LC-MS in which mass spectrometry is incorporated in HPLC as a detector has become widespread. Sodium alkanesulfonates, a general ion-pair reagent, being non-volatile crystals pose a problem in that they contaminate the interface. The IPC-PFFA series is made of highly volatile ion-pair reagents allowing for continuous LC-MS analysis without contaminating the interfaces.