Maintenance Notice (4:00 AM - 9:30 AM December 13, 11:30 PM December 13 - 1:40 AM December 14 2025): This website is scheduled to be unavailable due to maintenance. We appreciate your patience and understanding.
Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.200
Maximum quantity allowed is 999

Professor Paul J. Hergenrother
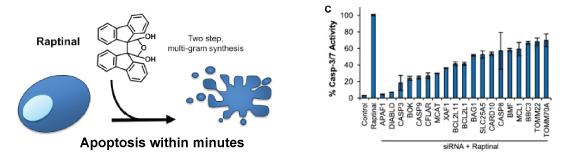
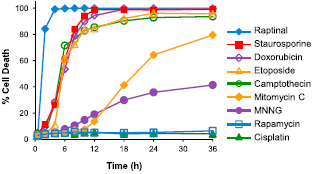
Raptinal has recently been shown to induce rapid apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway in multiple cell lines, and in whole organisms. Additionally, Raptinal shows tumor growth inhibition in vivo. Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death characterized by cell membrane blebbing followed by cell disassembly. Raptinal showed an average IC50 of 1.5 ± 0.3 μM across 22 cell lines after 24h of incubation, and was shown to release cytochrome c within minutes. Structural activity relationship assays against 25 small molecules showed Raptinal to be the best performer, with the presence of the aldehyde functionality being essential for the activity. The gene knockdown of known siRNA involved with intrinsic apoptosis pathway in cell lines increased cell survivability after Raptinal treatment, suggesting Raptinal’s mechanism of action with the intrinsic pathway. Further, incubation of cell lines with mitochondrial inhibitors afforded quantitative protection against Raptinal, indicating that mitochondrial function was essential for apoptosis to occur. Further, in whole organisms Raptinal induced cell apoptosis in live zebrafish, and showed tumor inhibition activity in mice while also not exhibiting hematological toxicity.