Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.199
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
Chemistry Chat
Technical Glossary | - Focusing on the Elements - Chemistry between Carbon and Other Elements
Carbene complex
Fischer carbene complexes show electrophilicity because the center metal is in an electron poor state. Therefore, the reactivity of it is similar to carbonyl compounds in which nucleophilic substitution of it with various nucleophiles proceeds. In addition one of substituents has to be an alkoxy group because of its electronic structure.
The chemical character of Schrock type carbene complexes is nucleophilic because of an electron rich state at the metal center. It shows especially high reactivities towards carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom multiple bonds. As typical chemical examples of Schrock type carbene complex usage, olefin metathesis and carbonyl olefination are well known. These synthetic characteristics are very useful so many suppliers have Schrock type carbene complexes as reagents.
Olefin metathesis
Olefin metathesis is a chemical reaction between double bonds of two separate olefin units in which double bonds exchange with each other to form two new olefin units. A Schrock type carbene complex is usually used for such a synthesis and Mo, Ru and Ti metals are generally used as active metals. The bulkiness of substituents on the olefins affects their reactivity in olefin metathesis, so the development of new carbene complexes showing higher reactivity has been studied since the 1990’s.
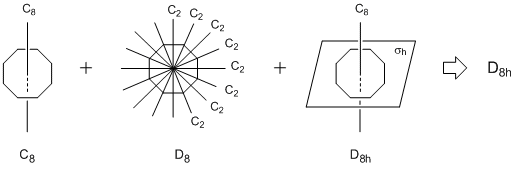
D8h symmetry
A molecule having a Cn principal rotation axis and its perpendicular n elements of C2 rotation axes is in the Dn group. In addition, a molecule having a σh mirror perpendicular to the principal axis shows Dnh symmetry. The molecule satisfying the conditions in the figure drawn below is in D8h group.