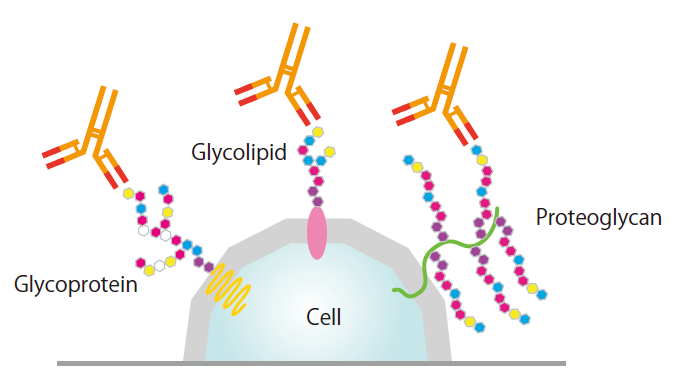
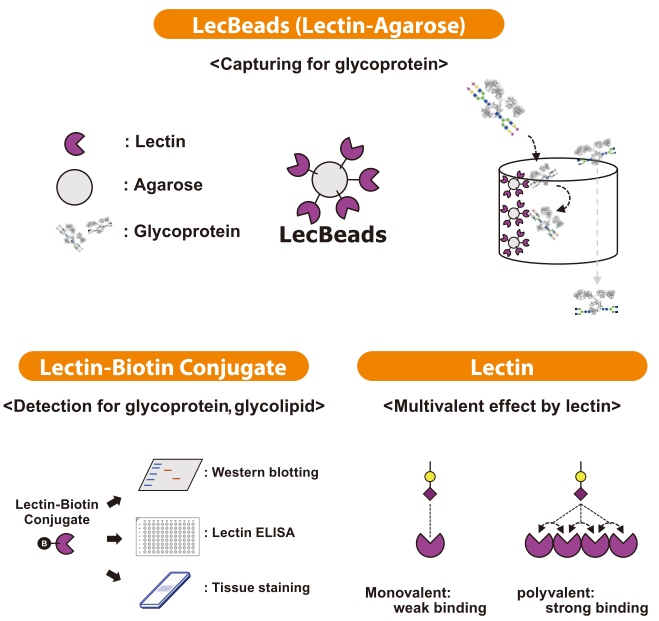
Make sure to sign up for an account today for exclusive coupons and free shipping on orders over $75!
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
Please select the quantity
| Product Number | A2872 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | A3143 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | L0169 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | A2505 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | A2506 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | A2507 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | A2508 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | A2509 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | A2510 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | A2576 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | A2578 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
| Product Number | A2580 |
| CAS RN | |
| Purity / Analysis Method: |
Product Number: A2872 |
Purity / Analysis Method:
Product Number: A3143 |
Purity / Analysis Method:
Product Number: L0169 |
Purity / Analysis Method:
Product Number: A2509 |
Purity / Analysis Method:
Product Number: A2510 |
Purity / Analysis Method:
Product Number: A2578 |
Purity / Analysis Method:
Added to Your Shopping Cart
Product Availability by Store Location
Hours