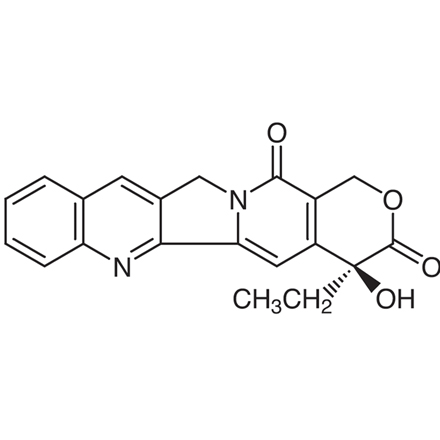
Camptothecin increases transduction by adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors.1)
Camptothecin (CPT), a plant alkaloid with antitumor activity, was first isolated by Wall
et al. in 1966 from the Chinese tree,
Camptotheca acuminate. CPT shows strong anticancer activity against a wide range of experimental tumors, but also low water solubility and high toxicity (myelosuppression and hemorrhagic cystitis). Because of these disadvantages, various CPT derivatives have been discovered such as irinotecan hydrochloride [
I0714] and topotecan. Camptotecin and its derivatives interfere with DNA synthesis by inhibiting the enzyme topoisomerase-I. In order to prevent and correct of topological problems caused by the DNA double helix, topoisomerase-I catalyzes the relaxation of negatively supercoiled DNA, the knotting and unknotting DNA and the linking complementary rings of single-stranded DNA into double-stranded rings. Then the inhibition action induces breaks in single strand DNA. Eventually, this leads to double-strand DNA breaks and apoptosis or cell death. (The product is for research purpose only.)