Sign up for free ground shipping on all website orders, no minimum required, and get exclusive coupons!
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
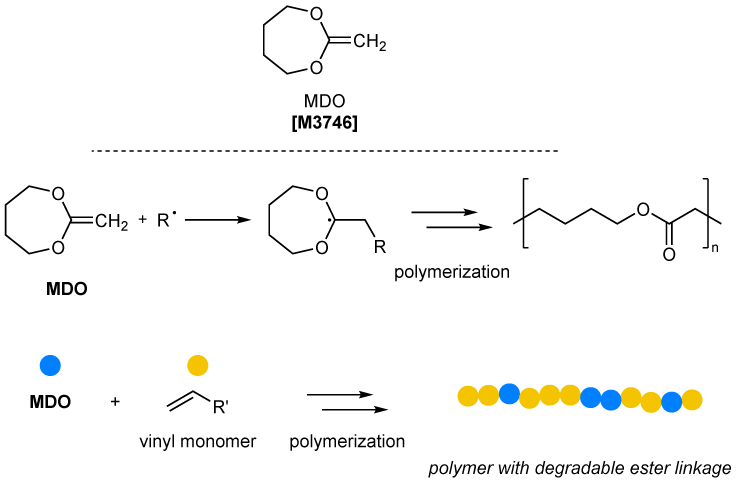
Cyclic Ketene Acetal Monomer Useful for the Development of Degradable Polymers
Cyclic ketene acetals (CKAs), such as 2-methylene-1,3-dioxepane (MDO), are monomers that can yield polyesters through radical ring-opening polymerization (rROP). Due to their ability to copolymerize with a broad range of vinyl monomers, CKAs have gained interest as a strategy to introduce highly degradable ester linkages into vinyl polymers. 1,2) Consequently, CKAs are expected to play a key role in developing polymers for biomedical applications, including therapeutic materials, as well as for addressing the issue of environmental accumulation of plastic waste. In the rROPs of CKAs, ring-retaining reactions can compete with rROP, but MDO is known to exhibit a high ring-opening efficiency due to its larger ring size. 3)
Related Products
References
- 1) 100th Anniversary of Macromolecular Science Viewpoint: Degradable Polymers from Radical Ring-Opening Polymerization: Latest Advances, New Directions, and Ongoing Challenges
- 2) Current Standing on Radical Ring-Opening Polymerizations of Cyclic Ketene Acetals as Homopolymers and Copolymers with One Another
- 3) Synthesis of Poly-ϵ-caprolactone via a Free Radical Mechanism. Free Radical Ring-Opening Polymerization of 2-Methylene-1,3-dioxepane

