Make sure to sign up for an account today for exclusive coupons and free shipping on orders over $75!
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
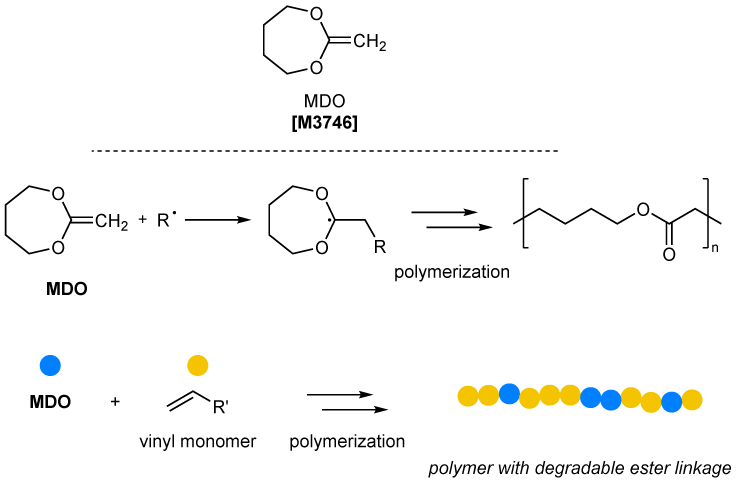
Cyclic Ketene Acetal Monomer Useful for the Development of Degradable Polymers
Cyclic ketene acetals (CKAs), such as 2-methylene-1,3-dioxepane (MDO), are monomers that can yield polyesters through radical ring-opening polymerization (rROP). Due to their ability to copolymerize with a broad range of vinyl monomers, CKAs have gained interest as a strategy to introduce highly degradable ester linkages into vinyl polymers. 1,2) Consequently, CKAs are expected to play a key role in developing polymers for biomedical applications, including therapeutic materials, as well as for addressing the issue of environmental accumulation of plastic waste. In the rROPs of CKAs, ring-retaining reactions can compete with rROP, but MDO is known to exhibit a high ring-opening efficiency due to its larger ring size. 3)
Related Products
References
- 1) 100th Anniversary of Macromolecular Science Viewpoint: Degradable Polymers from Radical Ring-Opening Polymerization: Latest Advances, New Directions, and Ongoing Challenges
- 2) Current Standing on Radical Ring-Opening Polymerizations of Cyclic Ketene Acetals as Homopolymers and Copolymers with One Another
- 3) Synthesis of Poly-ϵ-caprolactone via a Free Radical Mechanism. Free Radical Ring-Opening Polymerization of 2-Methylene-1,3-dioxepane

