Welcome to TCI Website! Reliable Quality Chemical Supplier!
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
Please select the quantity
CAS RN: 56-12-2 | Product Number: A0282
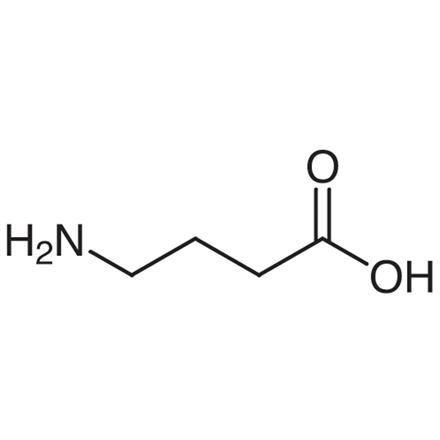
4-Aminobutyric Acid
Purity: >99.0%(T)
Synonyms:
- GABA
Product Documents:
| Size | Unit Price | Shanghai | Tianjin | Japan* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25G |
¥40.00
|
5 | 15 | ≥60 |
| 100G |
¥130.00
|
2 | 1 | 6 |
| 500G |
¥200.00
|
1 | 1 | ≥100 |
* For order or inquiry, please contact
Our Authorized Distributors.
*TCI frequently reviews storage conditions to optimize them. Please note that the latest information on the storage temperature for the products is described on our website.
* To send your quote request for bulk quantities, please click on the "Request Bulk Quote" button. Please note that we cannot offer bulk quantities for some products.
| Product Number | A0282 |
Purity / Analysis Method 
|
>99.0%(T) |
| Molecular Formula / Molecular Weight | C__4H__9NO__2 = 103.12 |
| Physical State (20 deg.C) | Solid |
Storage Temperature 
|
Room Temperature (Recommended in a cool and dark place, <15°C) |
| CAS RN | 56-12-2 |
| Reaxys Registry Number | 906818 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 87561936 |
| SDBS (AIST Spectral DB) | 1075 |
| Merck Index (14) | 430 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00008226 |
Specifications
| Appearance | White powder to crystaline |
| Purity(Nonaqueous Titration) | min. 99.0 % |
| Solubility in Water | almost transparency |
Properties (reference)
| Melting Point | 195 °C(dec.) |
GHS
Related Laws:
| RTECS# | ES6300000 |
Transport Information:
| Customs Control Conditions (Q) |
Application
GABA: A Major Inhibitory Neurotransmitter in Nervous System
4-Aminobutyric acid (γ-aminobutyric acid or GABA) is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in nervous system, the first report by Hayashi et al. in 1950s. GABA is present not only in the central nervous system but also in the peripheral nervous system. GABA plays the principal role in modulating neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system. Moreover, GABA is involved in a variety of biological functions such as proliferation, differentiation, migration and growth of neurons. GABA functions appear to be triggered by binding of GABA to its ionotropic receptors (GABAA and GABAC) which are ligand-gated chloride channels, and its metabotropic receptors GABAB which are coupled to G-proteins.
References
- Inhibition and excitation due to gamma-aminobutyric acid in the central nervous system.
- Excitatory actions of GABA during development: the nature of the nurture (a review)
- GABA and GABA receptors in the central nervous system and other organs (a review)
- GABA: a pioneer transmitter that excites immature neurons and generates primitive oscillations (a review)
- Extracellular level of GABA and Glu: in vivo microdialysis-HPLC measurements
- Determination and Comparison of γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Content in Pu-erh and Other Types of Chinese Tea
PubMed Literature
Documents
Product Articles
Product Documents (Note: Some products will not have analytical charts available.)
Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
Please select Language.
The requested SDS is not available.
Please Contact Us for more information.
Specifications
C of A & Other Certificates
Please enter Lot Number
Incorrect Lot Number. Please input only the 4-5 alphanumeric characters before the hyphen.
Sample C of A
This is a sample C of A and may not represent a recently manufactured lot of the product.
A sample C of A for this product is not available at this time.
Analytical Charts

Please enter Lot Number
Incorrect Lot Number. Please input only the 4-5 alphanumeric characters before the hyphen.
The requested analytical chart is not available. Sorry for the inconvenience.



