Maximum quantity allowed is 999
CAS RN: 82410-32-0 | Product Number: G0315
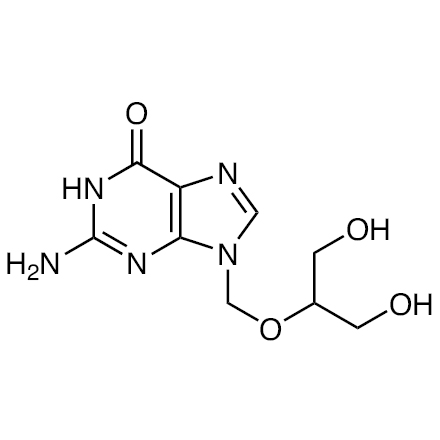
Ganciclovir
Purity: >98.0%(T)(HPLC)
- 9-[[2-Hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl]guanine
| Size | Unit Price | Hyderabad | Japan* | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5G |
₹12,500.00
|
2 | ≥100 |
|
| 25G |
₹19,100.00
|
3 | ≥40 |
|
*Upon orders receipt, Hyderabad stocks will be dispatched on the same day.
*Items available in Japan warehouse will be dispatched in 10-12 working days.
*INR price is exclusive of domestic taxes applicable.
*TCI frequently reviews storage conditions to optimize them. Please note that the latest information on the storage temperature for the products is described on our website.
Supplemental Product Information:
This product is a sample for RUO (research use only). Do not use this product for any purpose other than testing and research.
Previously this product had been labeled as a hydrate form both in product name and molecular formula. The hydrate form had no exclusive CAS RN and used to share the same CAS RN as the anhydrous form.
To avoid any misleading information and since moisture in product is considered as an impurity, we have decided to remove the term 'Hydrate' from product name and 'xH2O' from the molecular formula for such products.
Please use it at ease since there is no difference in product quality, even if you see the previous indications on a part of label.
| Product Number | G0315 |
Purity / Analysis Method 
|
>98.0%(T)(HPLC) |
| Molecular Formula / Molecular Weight | C__9H__1__3N__5O__4 = 255.23 |
| Physical State (20 deg.C) | Solid |
Storage Temperature 
|
Refrigerated (0-10°C) |
| Condition to Avoid | Heat Sensitive |
| CAS RN | 82410-32-0 |
| Reaxys Registry Number | 3654487 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 160871351 |
| Merck Index (14) | 4363 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00870588 |
| Appearance | White to Almost white powder to crystal |
| Purity(HPLC) | min. 98.0 area% |
| Purity(Nonaqueous Titration) | min. 98.0 %(calcd.on dried substance) |
| Drying loss | max. 4.0 % |
| Melting Point | 250 °C(dec.) |
| Degree of solubility in water | 4.3 g/l 25 °C |
| Pictogram |

|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H360 : May damage fertility or the unborn child. H340 : May cause genetic defects. H351 : Suspected of causing cancer. |
| Precautionary Statements | P501 : Dispose of contents/ container to an approved waste disposal plant. P202 : Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P201 : Obtain special instructions before use. P280 : Wear protective gloves/ protective clothing/ eye protection/ face protection. P308 + P313 : IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/ attention. P405 : Store locked up. |
| RTECS# | MF8407000 |
References
- Ganciclovir. A review of its antiviral activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy in cytomegalovirus infections
- Antiviral activity and mechanism of action of ganciclovir (a review)
- A protein kinase homolog controls phosphorylation of ganciclovir in human cytomegalovirus-infected cells
- Restoration of cytomegalovirus-specific CD4+ T-lymphocyte responses after ganciclovir and highly active antiretroviral therapy in individuals infected with HIV-1
- Antiviral drug resistance of human cytomegalovirus (a review)
References
- In vivo gene transfer with retroviral vector-producer cells for treatment of experimental brain tumors
- The "bystander effect": tumor regression when a fraction of the tumor mass is genetically modified
- S. M. Freeman, C. N. Abboud, K. A. Whartenby, C. H. Packman, D. S. Koeplin, F. L. Moolten, G. N. Abraham, Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 5274.
- Bystander killing of cancer cells by herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene is mediated by connexins
Documents
Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
The requested SDS is not available.
Please Contact Us for more information.
Specifications
C of A & Other Certificates
Sample C of A
A sample C of A for this product is not available at this time.
Analytical Charts

The requested analytical chart is not available. Sorry for the inconvenience.





